Blockchain technology’s first application was cryptocurrencies - positioned as a potential rival to government and central bank-controlled fiat currencies. However, providing the underlying technology that facilitates a viable alternative digital currency is just one of the many potential applications of Blockchain. The decentralized, p2p, cryptographically secured technology has been dubbed ‘the internet of value’, a compliment to the existing ‘internet of information’ that has underpinned the first epoch of the internet age. While ‘value’ is not necessarily only economic value, the finance industry is certainly one area that Blockchain technology is expected to hugely reshape in coming years.
Authentication, identification clearing, settling and record keeping have until now been the functions performed by financial services companies. And they’ve been handsomely rewarded for providing that service. However, now Blockchain’s digital ledger system has the potential to reduce or negate the need for financial services companies from banks to payment processing systems. Another way Blockchain has been referred to is as ‘a native medium for value’. It can be adapted to any kind of asset from money to company shares or even intellectual property assets. They can be stored, moved, transacted, exchanged and managed without powerful intermediaries being required to establish ‘trust’.
What are some of the specific ways in which Blockchain applications are already changing finance or can be expected to in the near future?
How Blockchain is Changing Banking
The potential for decentralized Blockchain applications within banking and finance can be seen as both a threat and opportunity to the industry. As a recent report on Blockchain in banking by consultancy firm Deloitte points out, banks are under pressure to lower costs and increase profitability. Regulatory and investor pressures, as well as the challenge being provided by non-banking fintech start-ups, mean the banking industry is finding it harder than ever before to maintain profitability. Integrating Blockchain-based systems could significantly help them in achieving operational efficiencies, reducing overheads.
Payment/transfer: traditional payment and transfer transactions rely heavily on counterparties. When you pay for something in a shop with a debit or credit card it’s an ‘at least’ six-step process involving a host of financial services companies. The diagram below, provided by Mastercard, demonstrates the complexity of the operation:
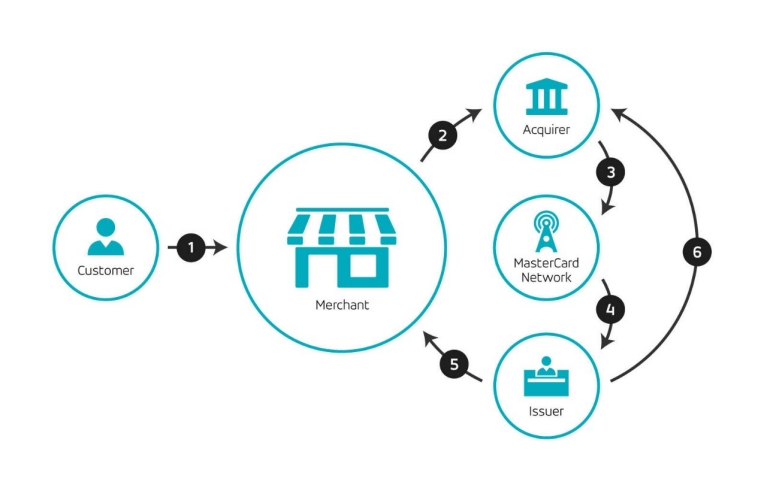
Transferring money from one bank account to another is similarly complex. Blockchain-based applications would cut out the need for all of these intermediaries and make payment, clearance, and settlement one action between a merchant and your bank account.
Identity: one of the most onerous roles banks have to contend with is verifying the identity of customers and counterparties. Regulators hold banks responsible for verifying that their customers are not using their services to launder money or any other criminal activity. Doing so is expensive and the fines handed out for failing to effectively even more so. There is currently a lot of work going on around Blockchain-based systems for customer identification, which have the potential to hugely reduce this burden for banks.
Personal data/financial history: Blockchain-based technology also holds significant potential when it comes to securely and efficiently unifying all of a customer’s personal data and financial history across different financial services. Bank customers could feed all of their financial transactions into one Blockchain-based digital briefcase. They would have control over their own data and financial history and give banks or other financial services access as requested and desired. Complex credit profile checks relying on 3rd party personal data aggregation would become redundant and processes such as applying for a loan much faster and easier.
Will Blockchain Replace Banks?
While Blockchain applications can be used by banks to make many processes more efficient, there is also the obvious question of whether they may not, eventually, make them redundant. If a decentralized Blockchain platform allows us to securely store money, make and receive payments very cheaply and almost instantly, why would we need a traditional bank at all?
Deloitte, in their report on how Blockchain is changing the banking sector, say they do not believe banks and financial intermediaries will be entirely replaced by the technology. It will hugely change how they work and make financial services companies far more efficient, and also less powerful. However, governments and the majority of the general public, are not in favor of complete decentralization and deregulation of financial systems and markets.
As such, for the foreseeable future banks and other financial services, companies will almost certainly still have a role to play.
How Blockchain is Changing Money and Business
What Blockchain will do is cut much of the fat out of financial and other business systems. Companies which perform the role of intermediaries in different transactions between counterparties will be looking over their shoulders. Blockchain’s potential will already be concerning financial intermediaries of the kind in the Mastercard diagram above. The days of transferring money to a relative abroad costing 10%, or e-payment wallets sucking up a significant percentage of transactions in and out of them are almost over. If provided with half an opportunity, Blockchain will democratize finance hugely in coming years.


